Overview:
Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL) remains resilient amid escalating supply chain disruptions, leveraging global diversification and innovation. However, critical dependencies on Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (NYSE: TSM) in Taiwan and logistical complexities in shifting away from China present substantial risks.
Key Insights:
- Tariff Impact & Cost Management:
- U.S. manufacturing relocation could increase iPhone production costs by over 30% due to higher labor expenses, limited skilled labor availability, and infrastructure constraints.
- Apple’s peak production involves approximately 250,000 workers per shift, complicating rapid geographic shifts.
- Phased product launches could ease concentrated supply chain pressures associated with annual September events.
- Supply Chain Diversification:
- Expansion into India, Vietnam, and Mexico is hindered by significant gaps in infrastructure, logistics, and manufacturing expertise.
- Automation advancements in stable product lines, such as AirPods, provide a blueprint for broader application, potentially reducing labor reliance.
- Geopolitical Risks (TSMC and Taiwan):
- Apple’s critical dependence on TSMC’s (NYSE: TSM) Taiwan operations is a substantial vulnerability, particularly due to Taiwan’s geopolitical tensions with China, risking severe disruption to chip supplies.
Key Manufacturing and Supply Chain Insights:
- Apple’s planned manufacturing shift from China to India will take 2-5 years minimum, even with substantial technological resources.
- Despite India’s labor costs being about 70% lower than China’s, overall manufacturing expenses in India are often higher due to factors like 30-40% lower productivity, infrastructure challenges, and regulatory complexities, thereby increasing the total cost per unit compared to China.
- Apple maintains high profitability with gross margins over 40%, driven by premium pricing and strong customer loyalty. While this profitability supports diversification efforts, increased production costs outside China present significant challenges.
- Apple is likely to maintain manufacturing operations in China for markets such as Europe, Canada, and Australia due to unmatched cost efficiencies.
- The success of Apple’s manufacturing transition significantly depends on partners like Foxconn building necessary infrastructure in India.
Apple is relatively well-positioned against supply disruptions but remains highly vulnerable due to its reliance on Taiwan (TSMC) for chip manufacturing.
Supply Chain and Manufacturing Challenges:
- Labor constraints, including limited skilled labor availability, significantly higher labor costs compared to Asia, and insufficient local expertise, make onshoring iPhone assembly to the U.S. highly impractical, though TSMC’s U.S. chip production benefits from automated processes.
- Apple manufactures approximately 200 million iPhones annually using around 250,000 workers per shift, two shifts daily.
- Breaking from Apple’s traditional September launch cadence would be challenging, though phasing or pushing back launches could mitigate supply constraints.
Additional Strategic and Technological Considerations:
- Apple’s dependency on TSMC in Taiwan represents its greatest risk due to potential geopolitical conflicts between Taiwan and China, posing threats of severe disruption to chip manufacturing capabilities essential for nearly all Apple products.
- The company prioritizes hardware margin protection, preferring to pressure suppliers before passing costs onto consumers.
- Apple customers display strong brand loyalty, typically tolerating modest price fluctuations, supported by Apple’s diverse product pricing strategies.
- Apple’s “Emergency SOS” via satellite indirectly highlights broader infrastructural dependencies, reinforcing Apple’s reliance on traditional cellular networks and components such as chips from Taiwan, thus making the company particularly sensitive to geopolitical and logistics disruptions.
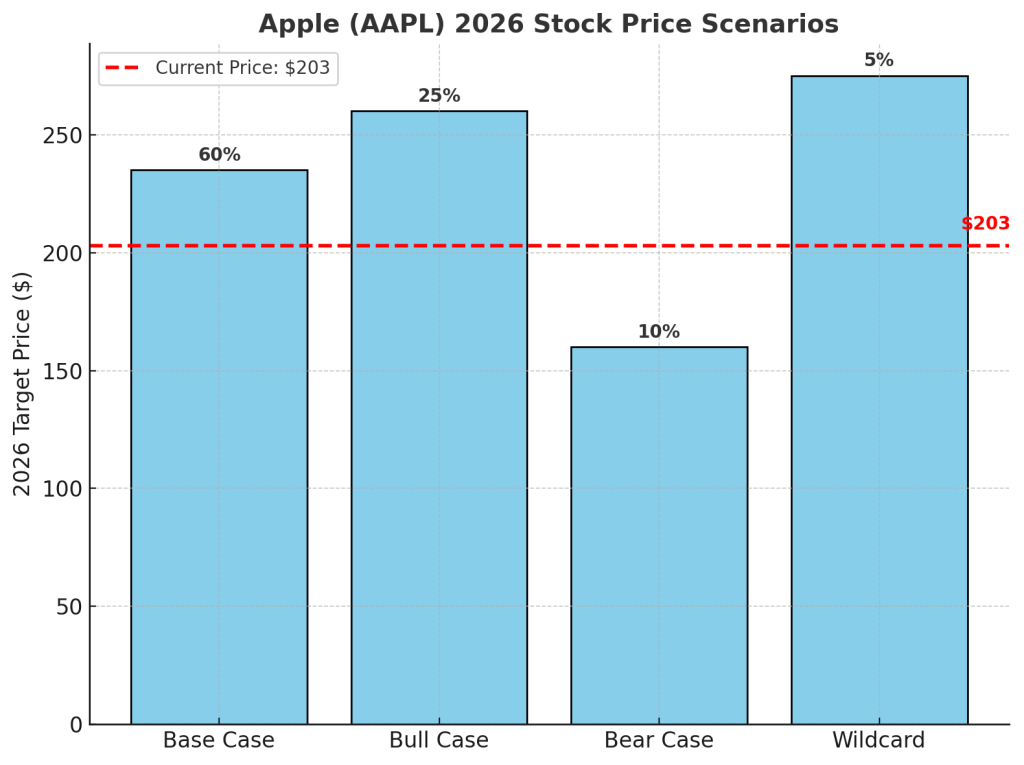
Stock Probability Map:
| Scenario | Probability | 2026 Price Target | Assumptions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Case: Partial diversification effective | 60% | $235 | Successful expansion into India and Vietnam partially offsets tariff impact |
| Bull Case: Tariffs stabilize, automation ramps up | 25% | $260 | Tariffs ease, efficient automation reduces costs, margins improve |
| Bear Case: Full decoupling mandated | 10% | $160 | Severe disruptions from forced reshoring, significantly higher production costs |
| Wildcard: Breakthrough in chip production automation | 5% | $275+ | Major innovation reduces reliance on Taiwan, significantly boosts investor confidence |
Current Price: $203 (as of May 21, 2025)
Peer Comparison:
- Qualcomm (NASDAQ: QCOM): Primarily a chip supplier; less impacted by assembly tariffs but shares geopolitical risks around Taiwan.
- TSMC (NYSE: TSM): Directly exposed to geopolitical risk with major operations in Taiwan. High automation reduces tariff impact but retains significant disruption risks.
- Samsung Electronics (KRX: 005930): Geographically diverse production mitigates some tariff impacts, though logistical challenges persist in scaling operations outside China.
Investor Fit Matrix:
| Investor Style | Fit | Approach |
| Growth | ✅ Good | Maintain/increase positions, capitalize on Apple’s brand strength, innovation, and strategic diversification. |
| Value | ✅ Good | Opportunistically invest during volatility, leveraging Apple’s financial resilience and proven operational strategies. |
| Risk-Averse | ⚠️ Cautious | Hedge due to significant geopolitical exposure; consider semiconductor ETFs (e.g., VanEck Semiconductor ETF (NASDAQ: SMH)) or more geographically diversified tech holdings. |
| ESG / Thematic | ⚠️ Cautious | Evaluate Apple’s sustainability efforts and labor practices; monitor progress on supply chain transparency and automation initiatives. Consider alternatives with stronger ESG profiles if progress is limited. |
Actionable Recommendations:
- Monitor geopolitical developments regarding Taiwan and updates from TSMC’s Arizona operations.
- Review Apple’s quarterly statements for strategic shifts and production insights.
- Hedge positions through semiconductor and automation-focused ETFs.
Bottom Line:
Apple’s innovative strategies position the company to effectively navigate geopolitical and tariff risks. Investors should closely monitor Apple’s diversification progress, consider hedging strategies through targeted ETFs (e.g., VanEck Semiconductor ETF (SMH)), and leverage volatility strategically (e.g., purchasing on significant price dips related to tariff news).